 RDO Springs - 10 Rue Benjamin Delessert - 60510 BRESLES - FRANCE
RDO Springs - 10 Rue Benjamin Delessert - 60510 BRESLES - FRANCE
Guide Ressorts de Traction
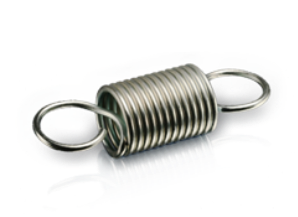
UNDERSTANDING TRACTION SPRINGS

The CETIM (Technical Center for Mechanical Industries) published in December 2002, a “guide for designers, users and manufacturers”, which concerns TRACTION SPRINGS. This very comprehensive 60-page document explains all the constraints that are subject to manufacturers for the production of parts. RDO springs actively participated in the definition of this document since one of our employees was a member of the working committee. We will show you here the main chapters of this document in order to better understand the essence of this document.
 |
 |
 |
The introduction recalls the distinction between the different types of springs:
-
- Hot: the steel tension spring is “forged” and then shaped. It undergoes quenching and tempering to keep the characteristics
- Cold: the steel tension spring is cold formed, and does not undergo any treatment after its manufacture other than stabilization in furnaces to preserve its technical characteristics.
-
RDO Springs manufactures cold wound extension springs.
On page 11, all definitions of technical terms used in the document are defined. The standard governing the manufacture of traction springs is:
The second part, (pages 14 to 24), explains all the characteristics of the TRACTION SPRINGS defined in standard NF EN 13906. Each chapter of the list below is commented on and the associated tables will allow you to better understand the requirements. . Field of application of the tension springs concerned by the technical elements explained in the document Calculation elements and more particularly the type of buckles (also called eyelets, or rings) but also if the end is in the form of hooks, or if the hooking end is made with attached parts).
Numerous case tables are then presented and will help you define the most common dimensions by presenting the calculation formulas (size, average diameter, winding ratio, tensions, stiffness, stress rate, maximum loads, number of turns, etc.) .
From page 26, a technical part related to the type of loop is covered. Indeed, it is essential to know the bending and torsional stresses of the loops which will be subjected directly to the forces. To aid in the design of the tension spring, a set of rules are laid out in order to “build” the tension spring with the most essential ribs. These dimensions are followed by tolerances on the desired winding ratio (taken from the German standard DIN 2097), according to the capability requirements (% of compliant parts in a batch).
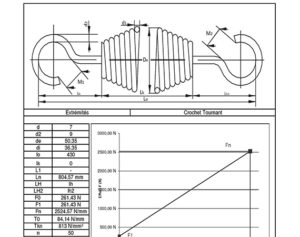
Reminder: Winding ratio = D / d, i.e. mean diameter of turns / nominal wire diameter Other tolerances are expressed on: the wire diameter to be used, the free length (empty), the length under load, the curl positions. Other suggestions are also expressed to define the context and conditions of use of the product. All of these elements will help fill in the technical data that will be used to establish the specifications for the manufacturer.
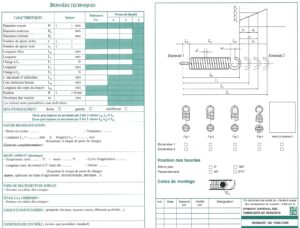
Note: We indicate many times on our website that not all types of springs are “standard”. Each user has their own characteristics and needs. They must be expressed and deduced from the allowable dimensions and tolerances. RDO is equipped and masters very technical software which allows it to define your plans according to your requirements.
Beginning on page 33, guidelines are expressed for:
- The choice of the material which will strongly influence the desired resistances. Assembly conditions: how will the product be assembled by the customer?
- Information on the appearance of the product The way in which the product will be controlled throughout its production process, and what are the specific coasts to control. Likewise, rigorous control and appropriate means are recommended (the manufacturer must comply with ISO 9000 standards).
- The manufacturing process: preparation of the material, shaping of the ends, heat treatment and surface treatment to finalize it.
- Known sources of fault Handling and packaging of springs

RDO SPRINGS respects all the recommendations of this guide and proves it via: Renewed ISO 9001 and EN 9100 certifications Its frequent customer audits of very demanding sectors such as the medical (pharma, medical, cosmetics), aeronautics & space sectors Its active participation in the training school for adjusters Its active participation in the UNM: Union for Standardization of Mechanics (https://www.unm.fr/fr/accueil) Its active participation in the union of French nationals (FIM Springs – Federation of Mechanical Industries –
We strongly advise you to consult this document because it recalls many rules and information for the designer, the manufacturer and the user. You can get it free of charge from CETIM (if you are affiliated with this organization) or directly from RDO SPRINGS. You can order the standards on the AFNOR (French Standardization Agency) website: https://www.boutique.afnor.org/recherche/resultats/mot/13906-2
 (+33) 3 44 07 34 34
(+33) 3 44 07 34 34 contact@rdosprings.com
contact@rdosprings.com


 NF EN 13906 -2: European Standard “Cylindrical helical springs manufactured from round wires and bars – Calculation and design – Part 2: tension springs” (September 2013).
NF EN 13906 -2: European Standard “Cylindrical helical springs manufactured from round wires and bars – Calculation and design – Part 2: tension springs” (September 2013). REQUEST FOR QUOTATION
REQUEST FOR QUOTATION download the brochure
download the brochure